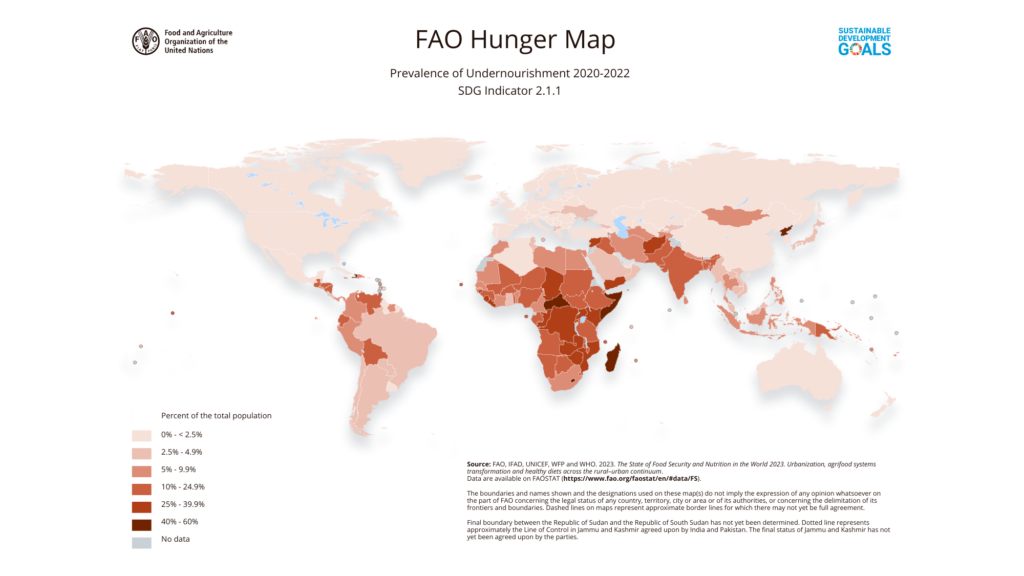
SDG 2 “no hunger” of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Hunger and malnutrition persist in many countries of the Global South producing agricultural commodities for global markets. The Food Security Standard helps companies involved in such agricultural production chains to fulfil their social responsibilities.
Focus

Team and Partners
The Food Security Standard and its approach will be continuously further consulted through a multi-stakeholder process, involving representatives of the private sector, the research sector, civil society, development organizations, sustainability certification schemes and administrations.
FSS Benefits
Food Security
Farmers, workers and local communities are food secure.
Human right
Producer of agricultural goods comply with the human right to food.
Due diligence
Retailer demonstrate due diligence in food security.
Sustainability
Consumers can opt for products that are also sustainable regarding food security.
Latest Publications

The Food Security Standard – Ensuring social sustainability in agricultural production
The Food Security Standard aims to support the private sector’s effort to end hunger and to improve social sustainability. It seeks to realize the right to adequate food through the responsible production and global trade of agricultural commodities.

FOSSEM – A stepwise approach
To fulfill the “Right to Food” and to achieve FSS certification, all criteria need to be complied with. However, complying with all requirements at once can be challenging for a farm and may take more time to achieve full compliance. In these situations, the FSS offers an alternative path: Food Security Sensitive Management (FOSSEM).

Upscaling the Right to Food through Certification
What happens if the Right to Food is violated in the very first step of the supply chain – where agricultural products like coffee, rubber or palm oil are grown? This happens in countries affected by hunger which produce products for global markets. The Food Security Standard (FSS) provides a solution: with this certification, the private sector can assess the local food security situation and showcase their commitment to human rights.